Safety Detect builds robust security capabilities, including system integrity check (SysIntegrity), app security check (AppsCheck), malicious URL check (URLCheck), fake user detection (UserDetect), and malicious Wi-Fi detection (WifiDetect), into your app, effectively protecting it against security threats.
SysIntegrity API: Checks whether the device running your app is secure, for example, whether it is rooted.
AppsCheck API: Obtains a list of malicious apps.
URLCheck API: Determines the threat type of a specific URL.
UserDetect API: Checks whether your app is interacting with a fake user.
WifiDetect API: Checks whether the Wi-Fi to be connected is secure.
In this codelab, you will use a created demo project to call the SysIntegrity, AppsCheck, URLCheck, UserDetect, and WifiDetect APIs.
Through the demo project, you will:
SysIntegrity:
AppsCheck:
URLCheck:
UserDetect:
WifiDetect:
In this codelab, you will learn how to:
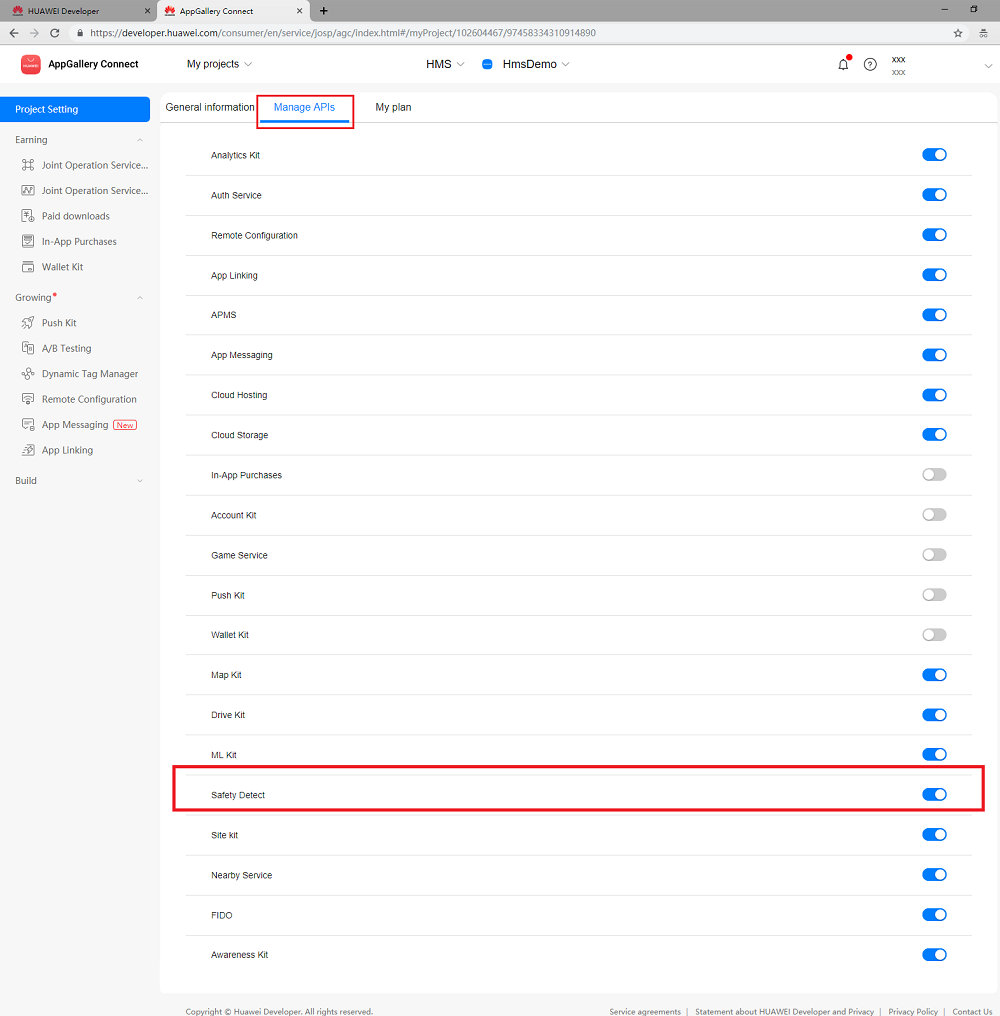
To integrate HUAWEI Safety Detect, you must complete the following preparations:
For details, please refer to Preparations for Integrating HUAWEI HMS Core.
dependencies {
// Add the following line
implementation 'com.huawei.hms:safetydetect:5.0.5.302'
}
Before building the APK, configure obfuscation scripts to prevent the HMS Core SDK from being obfuscated. If obfuscation arises, the HMS SDK may not function properly.
-ignorewarnings
-keepattributes *Annotation*
-keepattributes Exceptions
-keepattributes InnerClasses
-keepattributes Signature
-keepattributes SourceFile, LineNumberTable
-keep class com.hianalytics.android.** {*; }
-keep class com.huawei.updatesdk.** {*; }
-keep class com.huawei.hms.** {*; }
"R.string.hms*",
"R.string.connect_server_fail_prompt_toast",
"R.string.getting_message_fail_prompt_toast",
"R.string.no_available_network_prompt_toast",
"R.string.third_app_*",
"R.string.upsdk_*",
"R.layout.hms*",
"R.layout.upsdk_*",
"R.drawable.upsdk*",
"R.color.upsdk*",
"R.dimen.upsdk*",
"R.style.upsdk*"
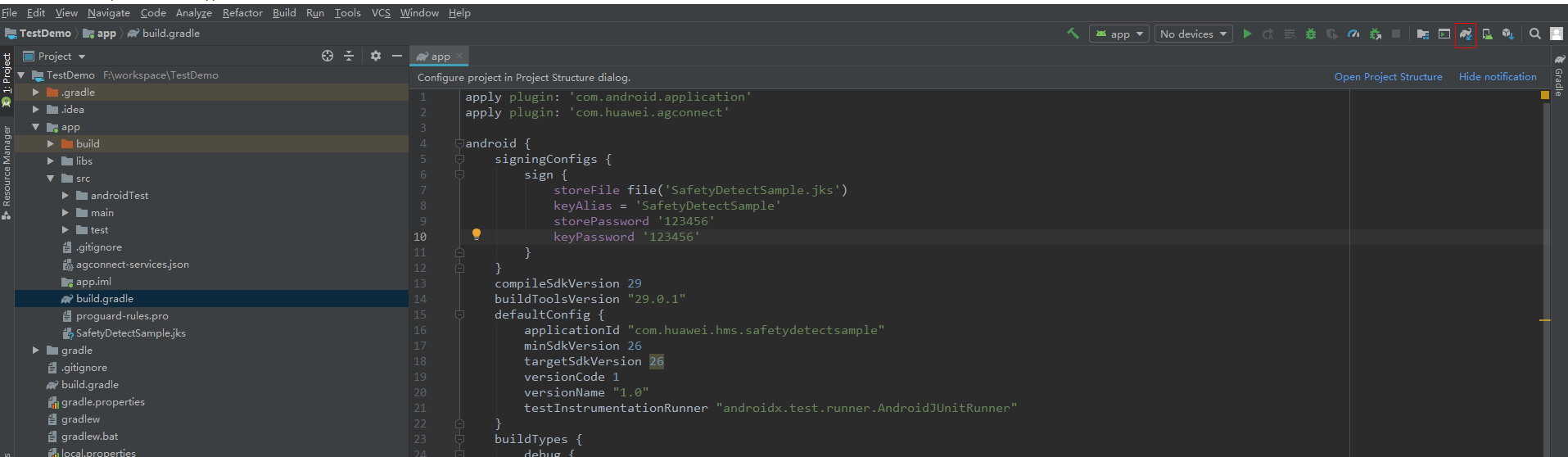
To call the SysIntegrity API, perform the following steps:
When calling the SysIntegrity API of Safety Detect, you must pass a nonce value that will be contained in the check result. You can check the nonce value to determine whether the returned result corresponds to your request and does not encounter replay attacks.
A nonce value must contain 16 to 66 bytes and can be used once only. It is recommended that the nonce value be derived from data sent to your server.
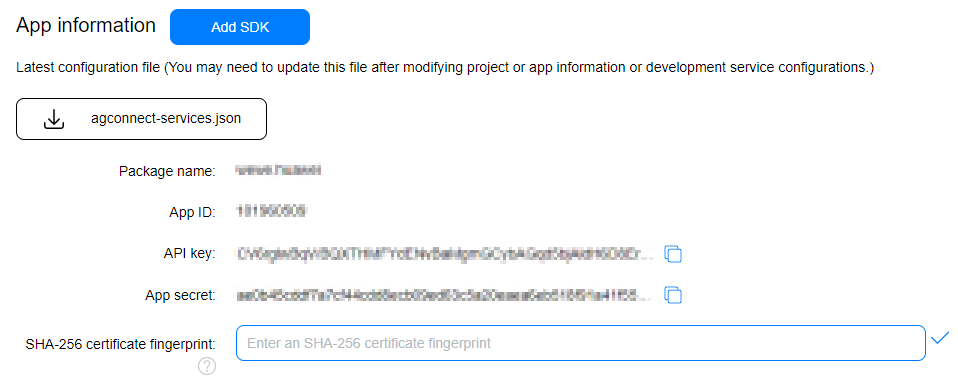
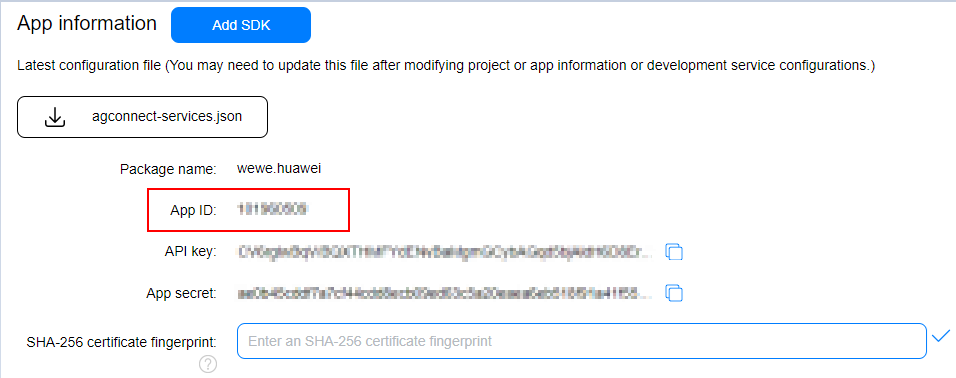
The SysIntegrity API has two input parameters. The first one is the nonce value, and the other is the app ID. To obtain the app ID, perform the following steps:
Java language:
private void invokeSysIntegrity() {
SafetyDetectClient mClient = SafetyDetect.getClient(Mainactivity.this);
// TODO(developer): Change the nonce generation to include your own, used once value,
// ideally from your remote server.
byte[] nonce = new byte[24];
try {
SecureRandom random;
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
random = SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong();
} else {
random = SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG");
}
random.nextBytes(nonce);
}
catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getMessage());
}
// TODO(developer): Change your app ID. You can obtain your app ID in AppGallery Connect.
Task task = mClient.sysIntegrity(nonce,"3*******");
task.addOnSuccessListener(new OnSuccessListener<SysIntegrityResp>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SysIntegrityResp response) {
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
// Use response.getResult() to get the result data.
String jwsStr = response.getResult();
}
}).addOnFailureListener(new OnFailureListener() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// An error occurred while communicating with the service.
if (e instanceof ApiException) {
// An error with the HMS API contains some
// additional details.
ApiException apiException = (ApiException) e;
// You can retrieve the status code using
// the apiException.getStatusCode() method.
Log.e(TAG, "Error: " + SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.getStatusCode()) + ": " + apiException.getMessage());
} else {
// A different, unknown type of error occurred.
Log.e(TAG, "ERROR:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
});
}
Kotlin language:
private fun invokeSysIntegrity() {
// TODO(developer): Change the nonce generation to include your own value.
val nonce = ByteArray(24)
try {
val random: SecureRandom = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong()
} else {
SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG")
}
random.nextBytes(nonce)
} catch (e: NoSuchAlgorithmException) {
Log.e(TAG, e.message)
}
// TODO(developer): Change your app ID. You can obtain your app ID in AppGallery Connect.
SafetyDetect.getClient(activity)
.sysIntegrity(nonce, APP_ID)
.addOnSuccessListener { response -> // Indicates communication with the service was successful.
// Use response.getResult() to get the result data.
val jwsStr = response.result
// Process the result data here
val jwsSplit = jwsStr.split(".").toTypedArray()
val jwsPayloadStr = jwsSplit[1]
val payloadDetail = String(Base64.decode(jwsPayloadStr.toByteArray(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), Base64.URL_SAFE), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
try {
val jsonObject = JSONObject(payloadDetail)
val basicIntegrity = jsonObject.getBoolean("basicIntegrity")
fg_button_sys_integrity_go.setBackgroundResource(if (basicIntegrity) R.drawable.btn_round_green else R.drawable.btn_round_red)
fg_button_sys_integrity_go.setText(R.string.rerun)
val isBasicIntegrity = basicIntegrity.toString()
val basicIntegrityResult = "Basic Integrity: $isBasicIntegrity"
fg_payloadBasicIntegrity.text = basicIntegrityResult
if (!basicIntegrity) {
val advice = "Advice: " + jsonObject.getString("advice")
fg_payloadAdvice.text = advice
}
} catch (e: JSONException) {
val errorMsg = e.message
Log.e(TAG, errorMsg ?: "unknown error")
}
}
.addOnFailureListener { e -> // There was an error communicating with the service.
val errorMsg: String?
errorMsg = if (e is ApiException) {
// An error with the HMS API contains some additional details.
val apiException = e as ApiException
SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.statusCode) +
": " + apiException.message
// You can use the apiException.getStatusCode() method to get the status code.
} else {
// unknown type of error has occurred.
e.message
}
Log.e(TAG, errorMsg)
Toast.makeText(activity?.applicationContext, errorMsg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
fg_button_sys_integrity_go.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.btn_round_yellow)
fg_button_sys_integrity_go.setText(R.string.rerun)
}
}
It is recommended that the JWS-format result be handled in the following process. The certificate and signature verification needs to be implemented on the background server of your app.
{
"advice":"RESTORE_TO_FACTORY_ROM",
"apkCertificateDigestSha256":[
"yT5JtXRgeIgXssx1gQTsMA9GzM9ER4xAgCsCC69Fz3I="
],
"apkDigestSha256":"6Ihk8Wcv1MLm0O5KUCEVYCI/0KWzAHn9DyN38R3WYu8=",
"apkPackageName":"com.huawei.hms.safetydetectsample",
"basicIntegrity":false,
"nonce":"R2Rra24fVm5xa2Mg",
"timestampMs":1571708929141
}
For details about the verification logic, click safety-detect-server-sample to download the sample code.
Install the sample APK to be tested, and tap SysIntegrity and then the test button.
You can directly call the getMaliciousApps method of the AppsCheck API to obtain a list of malicious apps:
Java language:
private void invokeGetMaliciousApps() {
SafetyDetectClient appsCheckClient = SafetyDetect.getClient(MainActivity.this);
Task task = appsCheckClient.getMaliciousAppsList();
task.addOnSuccessListener(new OnSuccessListener<MaliciousAppsListResp>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(MaliciousAppsListResp maliciousAppsListResp) {
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
// Use resp.getMaliciousApps() to get malicious apps data.
List<MaliciousAppsData> appsDataList = maliciousAppsListResp.getMaliciousAppsList();
// Indicates get malicious apps was successful.
if (maliciousAppsListResp.getRtnCode() == CommonCode.OK) {
if (appsDataList.isEmpty()) {
// Indicates there are no known malicious apps.
Log.i(TAG, "There are no known potentially malicious apps installed.");
} else {
Log.i(TAG, "Potentially malicious apps are installed!");
for (MaliciousAppsData maliciousApp : appsDataList) {
Log.i(TAG, "Information about a malicious app:");
// Use getApkPackageName() to get APK name of malicious app.
Log.i(TAG, "APK: " + maliciousApp.getApkPackageName());
// Use getApkSha256() to get APK sha256 of malicious app.
Log.i(TAG, "SHA-256: " + maliciousApp.getApkSha256());
// Use getApkCategory() to get category of malicious app.
// Categories are defined in AppsCheckConstants
Log.i(TAG, "Category: " + maliciousApp.getApkCategory());
}
}
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "getMaliciousAppsList fialed: " + maliciousAppsListResp.getErrorReason());
}
}
}).addOnFailureListener(new OnFailureListener() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// An error occurred while communicating with the service.
if (e instanceof ApiException) {
// An error with the HMS API contains some
// additional details.
ApiException apiException = (ApiException) e;
// You can retrieve the status code using the apiException.getStatusCode() method.
Log.e(TAG, "Error: " + SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.getStatusCode()) + ": " + apiException.getStatusMessage());
} else {
// A different, unknown type of error occurred.
Log.e(TAG, "ERROR: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
});
}
Kotlin language:
private fun getMaliciousApps() {
SafetyDetect.getClient(activity)
.maliciousAppsList
.addOnSuccessListener { maliciousAppsListResp ->
val appsDataList: List<MaliciousAppsData> = maliciousAppsListResp.maliciousAppsList
if (maliciousAppsListResp.rtnCode == CommonCode.OK) {
if (appsDataList.isEmpty()) {
val text = "No known potentially malicious apps are installed."
Toast.makeText(activity!!.applicationContext, text, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
for (maliciousApp in appsDataList) {
Log.e(TAG, "Information about a malicious app:")
Log.e(TAG, " APK: " + maliciousApp.apkPackageName)
Log.e(TAG, " SHA-256: " + maliciousApp.apkSha256)
Log.e(TAG, " Category: " + maliciousApp.apkCategory)
}
val maliciousAppAdapter: ListAdapter = MaliciousAppsDataListAdapter(appsDataList, requireContext())
fg_list_app.adapter = maliciousAppAdapter
}
} else {
val msg = ("Get malicious apps list failed! Message: "
+ maliciousAppsListResp.errorReason)
Log.e(com.huawei.hms.safetydetect.sample.SafetyDetectAppsCheckAPIFragment.TAG, msg)
Toast.makeText(activity!!.applicationContext, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
.addOnFailureListener { e -> // There was an error communicating with the service.
val errorMsg: String?
errorMsg = if (e is ApiException) {
// An error with the HMS API contains some additional details.
val apiException = e as ApiException
SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.statusCode) +
": " + apiException.message
// You can use the apiException.getStatusCode() method to get the status code.
} else {
// Unknown type of error has occurred.
e.message
}
val msg = "Get malicious apps list failed! Message: $errorMsg"
Log.e(com.huawei.hms.safetydetect.sample.SafetyDetectAppsCheckAPIFragment.TAG, msg)
Toast.makeText(activity!!.applicationContext, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
Install the sample APK to be tested, and tap AppsCheck and then GET HARMFUL APPS LIST.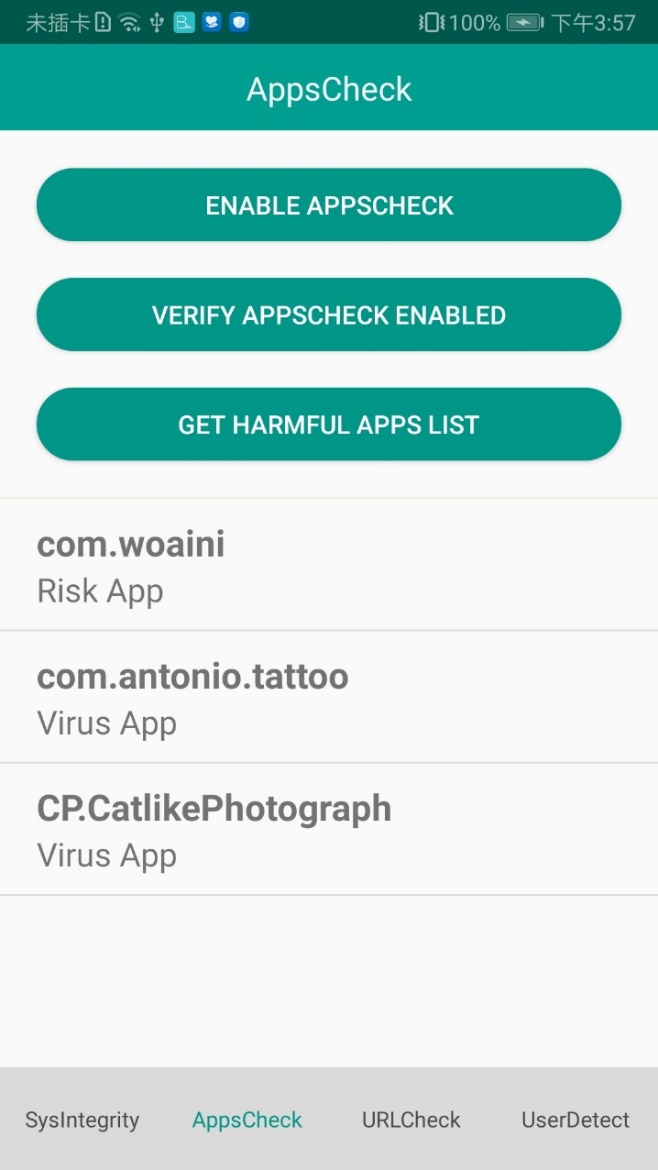
To call the URLCheck API, perform the following steps:
Before using the URLCheck API, you must call the initUrlCheck() method to initialize the API. The sample code is as follows:
Java language:
SafetyDetectClient client = SafetyDetect.getClient(getActivity());
client.initUrlCheck();
Kotlin language:
client = SafetyDetect.getClient(activity)
client.initUrlCheck()
Specify the types of concerned threats as the input parameter of the URLCheck API. Constants in the UrlCheckThreat class contain the supported threat types.
package com.huawei.hms.safetydetect;
public class UrlCheckThreat {
/**
* URLs of this type are marked as URLs of pages containing potentially malicious apps (such as home page tampering URLs, Trojan-infected URLs, and malicious app download URLs).
*/
public static final int MALWARE = 1;
/**
* URLs of this type are marked as phishing and spoofing URLs.
*/
public static final int PHISHING = 3;
}
Initiate a URL check request. The URL to be checked contains the protocol, host, and path but does not contain the query parameter. The sample code is as follows:
Java language:
String url = "https://developer.huawei.com/consumer/cn/";
SafetyDetect.getClient(this).urlCheck(url, appId, UrlCheckThreat.MALWARE, UrlCheckThreat.PHISHING).addOnSuccessListener(this, new OnSuccessListener<UrlCheckResponse >(){
@Override
public void onSuccess(UrlCheckResponse urlResponse) {
if (urlResponse.getUrlCheckResponse().isEmpty()) {
// No threat exists.
} else {
// Threats exist.
}
}
}).addOnFailureListener(this, new OnFailureListener() {
@Override
public void onFailure(@NonNull Exception e) {
// An error occurred during communication with the service.
if (e instanceof ApiException) {
// HMS Core (APK) error code and corresponding error description.
ApiException apiException = (ApiException) e;
Log.d(TAG, "Error: " + CommonStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.getStatusCode()));
// Note: If the status code is SafetyDetectStatusCode.CHECK_WITHOUT_INIT,
// you did not call the initUrlCheck() method or you have initiated a URL check request before the call is completed.
// If an internal error occurs during the initialization, you need to call the initUrlCheck() method again to initialize the API.
} else {
// An unknown exception occurs.
Log.d(TAG, "Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}); });
Kotlin language:
val url = "https://developer.huawei.com/consumer/cn/"
client.urlCheck(
url,
APP_ID, // Specify url threat type
UrlCheckThreat.MALWARE,
UrlCheckThreat.PHISHING
).addOnSuccessListener {
val list = it.urlCheckResponse
if (list.isEmpty()) {
// No threat exists.
} else {
// Threats exist.
}
}.addOnFailureListener {
// An error occurred during communication with the service.
if (it is ApiException) {
// HMS Core (APK) error code and corresponding error description.
val apiException = it
Log.d(
TAG,
"Error: " + CommonStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.statusCode)
)
// Note: If the status code is SafetyDetectStatusCode.CHECK_WITHOUT_INIT,
// you did not call the initUrlCheck() method or you have initiated a URL check request before the call is completed.
// If an internal error occurs during the initialization, you need to call the initUrlCheck() method again to initialize the API.
} else {
// An unknown exception occurs.
Log.d(TAG, "Error: " + it.message)
}
}
Call the getUrlCheckResponse() method of the URLCheckResponse object to obtain the URL check response. The method returns List<UrlCheckThreat> which contains a list of all detected URL threat types. If the list is empty, no threat has been detected. Otherwise, you can call the getUrlCheckResult () method of UrlCheckThreat to obtain the specific threat code. The sample code is as follows:
Java language:
final EditText testRes = getActivity().findViewById(R.id.fg_call_urlResult);
List<UrlCheckThreat> list = urlCheckResponse.getUrlCheckResponse();
if (list.isEmpty()) {
testRes.setText("ok");
}
else{
for (UrlCheckThreat threat : list) {
int type = threat.getUrlCheckResult();
}
}
Kotlin language:
val list = it.urlCheckResponse
if (list.isEmpty()) {
fg_call_urlResult.text = Editable.Factory.getInstance().newEditable("ok")
} else {
for (threat in list) {
val type = threat.urlCheckResult
}
}
If your app does not need to call the URLCheck API anymore or will not need to for a while, you can call the shutdownUrlCheck() method to close the URL check session and release relevant resources.
SafetyDetect.getClient(this).shutdownUrlCheck();
Install the sample APK to be tested, and tap URLCheck and then CHECK URL.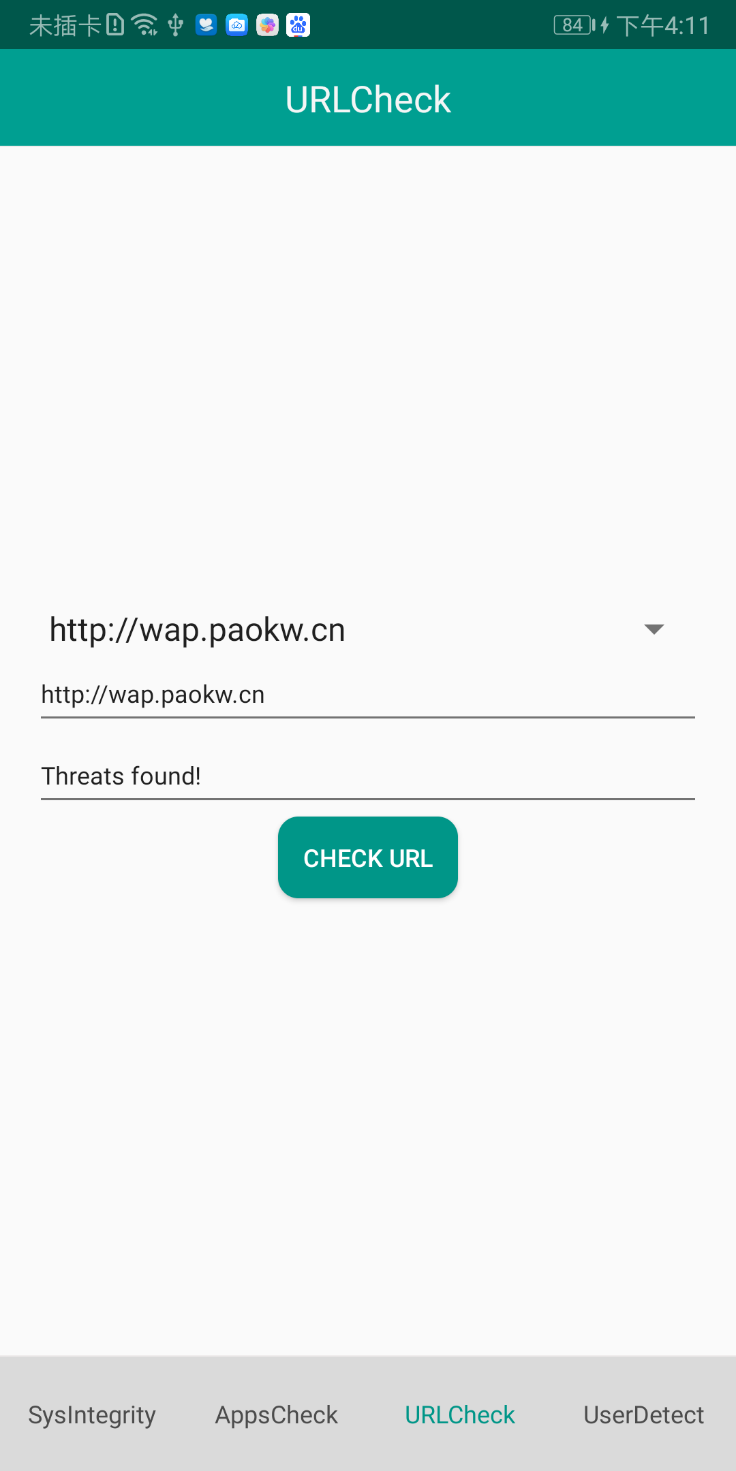
The sample code consists of two parts: client and server. The client part demonstrates how to call the API and obtain a response token. The server part demonstrates how to obtain the final fake user detection result.
To call the UserDetect API, perform the following steps:
The UserDetect API provides the behavior detection capability. To use the capability, you can call the initUserDetect() method to initialize fake user detection. The sample code is as follows:
Java language:
// Replace with your activity or context as a parameter.
SafetyDetectClient client = SafetyDetect.getClient(MainActivity.this);
client.initUserDetect().addOnSuccessListener(new OnSuccessListener<Void>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Void v) {
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
}
}).addOnFailureListener(new OnFailureListener() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// There was an error communicating with the service.
}
});
Kotlin language:
private fun initUserDetect() {
// Replace with your activity or context as a parameter.
val client = SafetyDetect.getClient(this@MainActivity)
client.initUserDetect().addOnSuccessListener {
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
}.addOnFailureListener {
// There was an error communicating with the service.
}
}
You need to call the userDetection method to initiate a detection request. Generally, this method is triggered when a user taps a UI control (such as a button). To call the userDetection method, perform the following steps:
The sample code for calling this method is as follows:
Java language:
public void onClick(View v) {
SafetyDetectClient client = SafetyDetect.getClient(getActivity());
String appId = "your_app_id";
client.userDetection(appId)
.addOnSuccessListener(new OnSuccessListener<UserDetectResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(UserDetectResponse userDetectResponse) {
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
String responseToken = userDetectResponse.getResponseToken();
if (!responseToken.isEmpty()) {
// Send the response token to your app server, and call the cloud API of HMS Core on your server to obtain the fake user detection result.
}
}
})
.addOnFailureListener(new OnFailureListener() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// There was an error communicating with the service.
String errorMsg;
if (e instanceof ApiException) {
// An error with the HMS API contains some additional details.
// You can use the apiException.getStatusCode() method to get the status code.
ApiException apiException = (ApiException) e;
errorMsg = SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.getStatusCode()) + ": "
+ apiException.getMessage();
} else {
// Unknown type of error has occurred.
errorMsg = e.getMessage();
}
Log.i(TAG, "User detection fail. Error info: " + errorMsg);
}
});
}
Kotlin language:
override fun onClick(v: View?) {
val client = SafetyDetect.getClient(activity)
val appId = "your_app_id"
client.userDetection(appId)
.addOnSuccessListener { userDetectResponse ->
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
val responseToken = userDetectResponse.responseToken
if (responseToken.isNotEmpty()) {
// Send the response token to your app server, and call the cloud API of HMS Core on your server to obtain the fake user detection result.
}
}
.addOnFailureListener { // There was an error communicating with the service.
val errorMsg: String? = if (it is ApiException) {
// An error with the HMS API contains some additional details.
// You can use the apiException.getStatusCode() method to get the status code.
(SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(it.statusCode) + ": "
+ it.message)
} else {
// Unknown type of error has occurred.
it.message
}
Log.i(TAG, "User detection fail. Error info: $errorMsg")
}
}
Perform the following steps on the server:
POST https://hirms.cloud.huawei.com/rms/v1/userRisks/verify?appId=****** HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8
{{
"accessToken":"AAWWHI94sgUR2RU5_P1ZptUiwLq7W8XWJO2LxaAPuXw4_HOJFXnBlN-q5_3bwlxVW_SHeDPx_s5bWW-9DjtWZsvcm9CwXe1FHJg0u-D2pcQPcb3sTxDTJeiwEb9WBPl_9w",
"response":"1_55d74c04eab36a0a018bb7a879a6f49f072b023690cba936"
}
For details about the request API, please refer to API Reference.
Call the shutdownUserDetect() method to disable UserDetect and release resources. The sample code is as follows:
Java language:
// Replace with your activity or context as a parameter.
SafetyDetectClient client = SafetyDetect.getClient(MainActivity.this);
client.shutdownUserDetect().addOnSuccessListener(new OnSuccessListener<Void>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Void v) {
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
}
}).addOnFailureListener(new OnFailureListener() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// There was an error communicating with the service.
}
});
Kotlin language:
private fun shutdownUserDetect() {
// Replace with your activity or context as a parameter.
val client = SafetyDetect.getClient(this@MainActivity)
client.shutdownUserDetect()
.addOnSuccessListener {
// Indicates communication with the service was successful.
}.addOnFailureListener {
// There was an error communicating with the service.
}
}
Install the sample APK to be tested, tap UserDetect and then LOGIN, and complete login as prompted.
|
|
The sample code demonstrates how to call the WifiDetect API and obtain the detection result.
You can directly call getWifiDetectStatus() of SafetyDetectClient to obtain the malicious Wi-Fi detection result.
Java language:
private void invokeGetWifiDetectStatus() {
Log.i(TAG, "Start to getWifiDetectStatus!");
SafetyDetectClient wifidetectClient = SafetyDetect.getClient(getApplicationContext());
Task task = wifidetectClient.getWifiDetectStatus();
task.addOnSuccessListener(new OnSuccessListener<WifiDetectResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(WifiDetectResponse wifiDetectResponse) {
int wifiDetectStatus = wifiDetectResponse.getWifiDetectStatus();
Log.i(TAG, "\n-1: Failed to obtain the Wi-Fi status. \n" + "0: No Wi-Fi is connected. \n" + "1: The connected Wi-Fi is secure. \n" + "2: The connected Wi-Fi is insecure.");
Log.i(TAG, "wifiDetectStatus is: " + wifiDetectStatus);
}
}).addOnFailureListener(new OnFailureListener() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
if (e instanceof ApiException) {
ApiException apiException = (ApiException) e;
Log.e(TAG,
"Error: " + apiException.getStatusCode() + ":"
+ SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.getStatusCode()) + ": "
+ apiException.getStatusMessage());
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "ERROR! " + e.getMessage());
}
}
});
}
Kotlin language:
private val wifiDetectStatus: Unit
private get() {
SafetyDetect.getClient(activity)
.wifiDetectStatus
.addOnSuccessListener { wifiDetectResponse ->
val wifiDetectStatus = wifiDetectResponse.wifiDetectStatus
val wifiDetectView = "WifiDetect status: $wifiDetectStatus"
fg_wifidetecttextView.text = wifiDetectView
}
.addOnFailureListener { e -> // There was an error communicating with the service.
val errorMsg: String?
errorMsg = if (e is ApiException) {
// An error with the HMS API contains some additional details.
val apiException = e
(SafetyDetectStatusCodes.getStatusCodeString(apiException.statusCode) + ": "
+ apiException.message)
// You can use the apiException.getStatusCode() method to get the status code.
} else {
// Unknown type of error has occurred.
e.message
}
val msg = "Get wifiDetect status failed! Message: $errorMsg"
Log.e(TAG, msg)
fg_wifidetecttextView.text = msg
}
}
Install the sample APK to be tested, tap WifiDetect and then GET WIFIDETECT STATUS.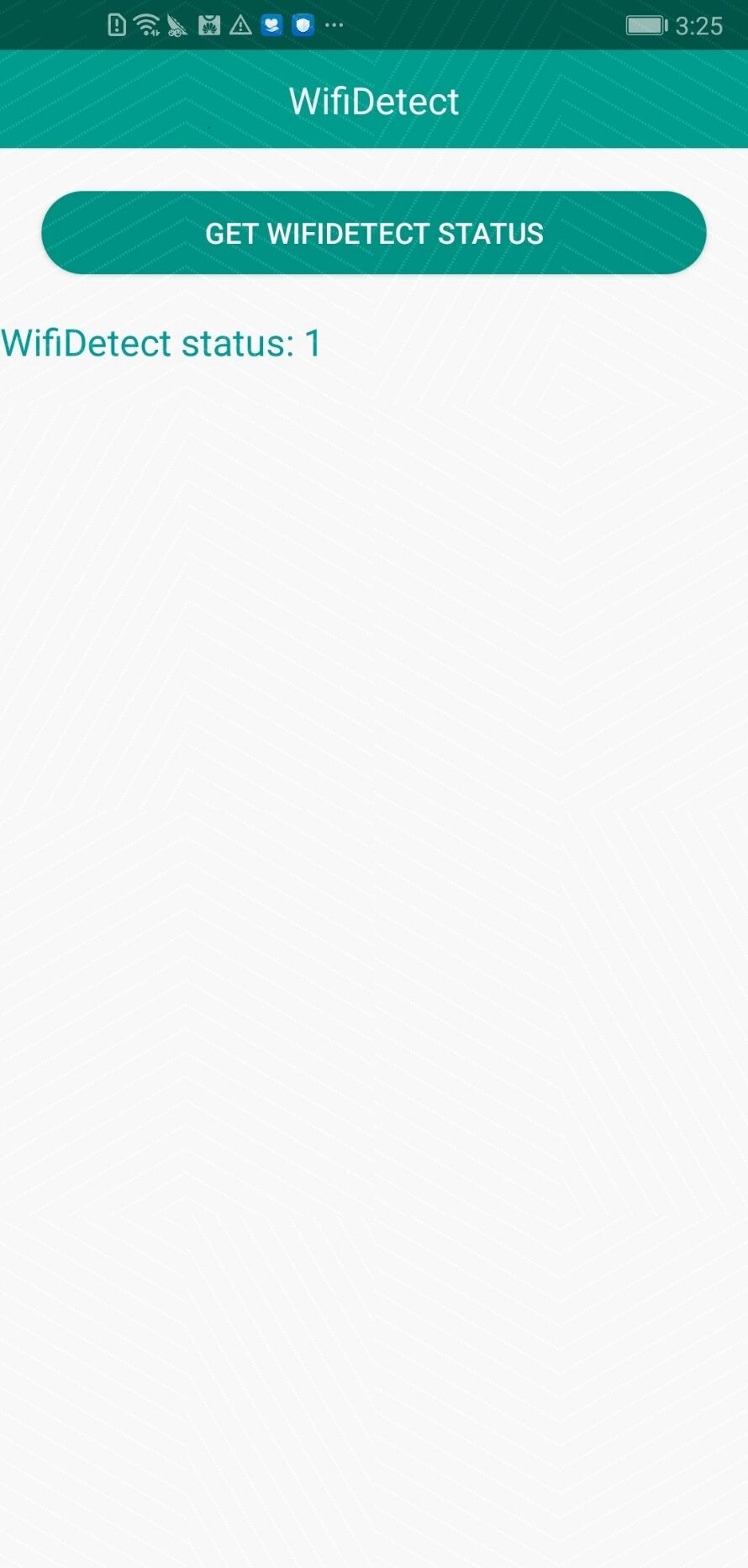
Well done. You have successfully completed this codelab and learned how to:
For more information, please click the following link:
Related Documents
You can click the button below to download the source code.