Cloud Functions enables serverless computing. It provides the Function as a Service (FaaS) capabilities to simplify app development and O&M so your functions can be implemented more easily and your service capabilities can be built more quickly.
In this codelab, you can build a function that can interact with your app using Cloud Functions. To do so, you will need to:
An iPhone or a simulator for testing
To integrate Cloud Functions of AppGallery Connect, you must complete the following preparations:
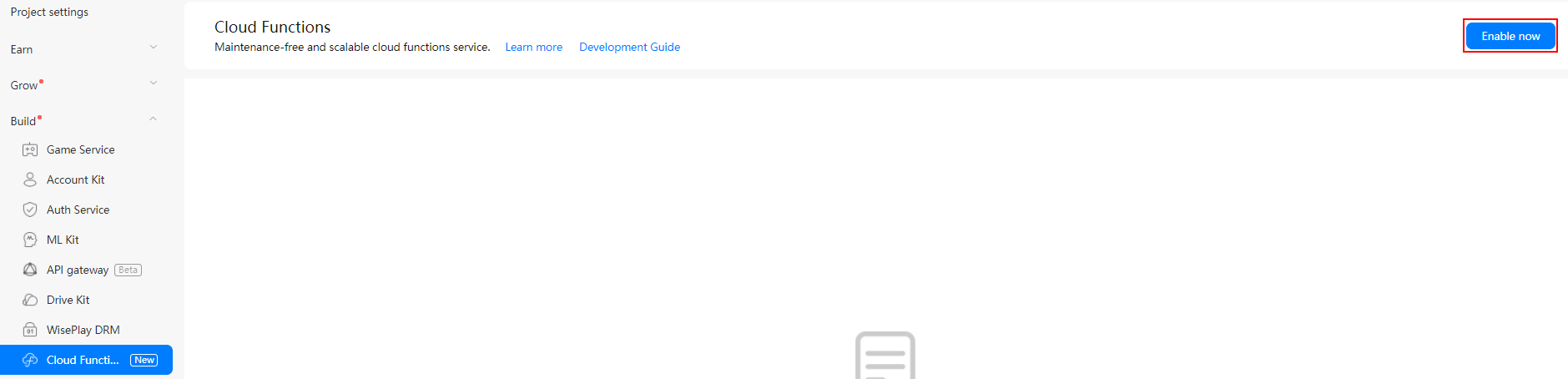
You can use CocoaPods to integrate the Cloud Functions SDK in Xcode.
cd project-directory
pod init
target 'AGC-Function-1' do
pod 'AGConnectFunction'
end
pod install
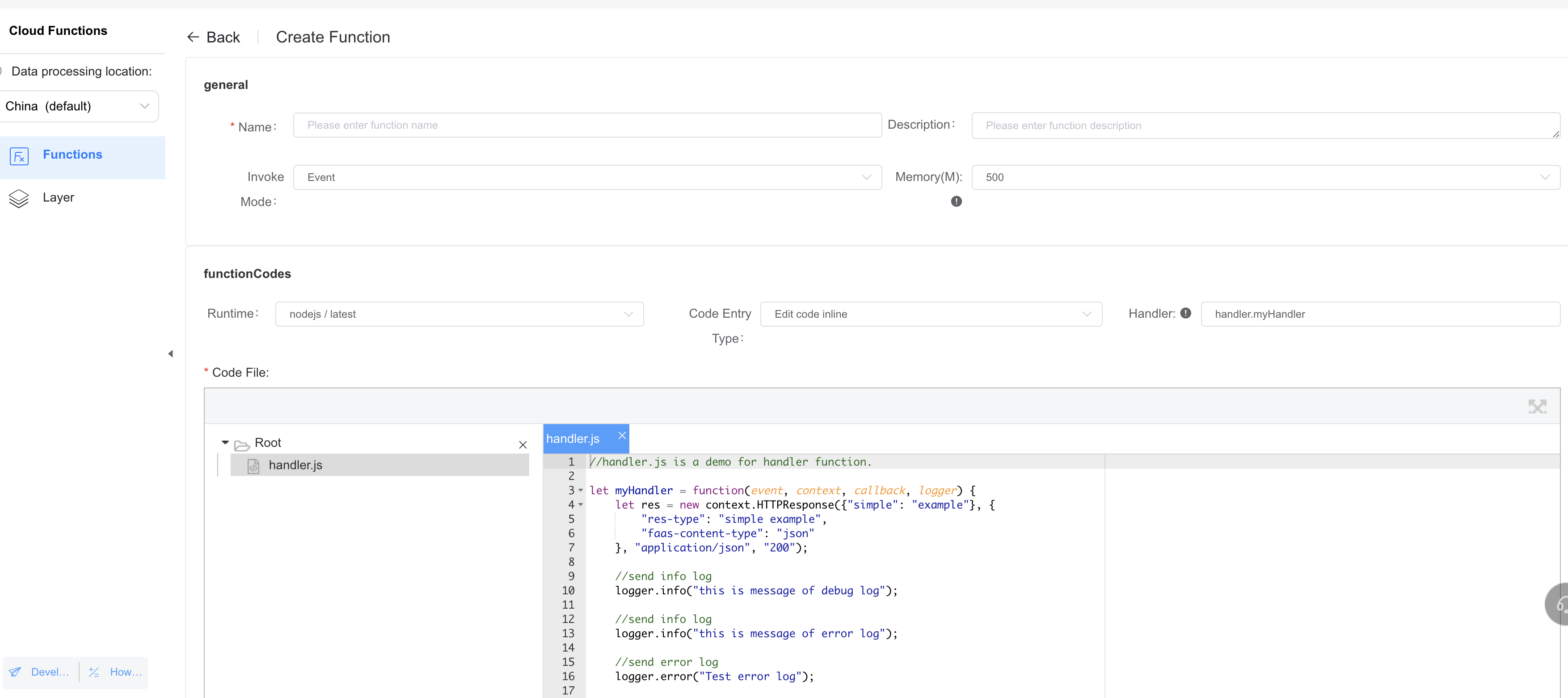
The following figure shows the result after installation.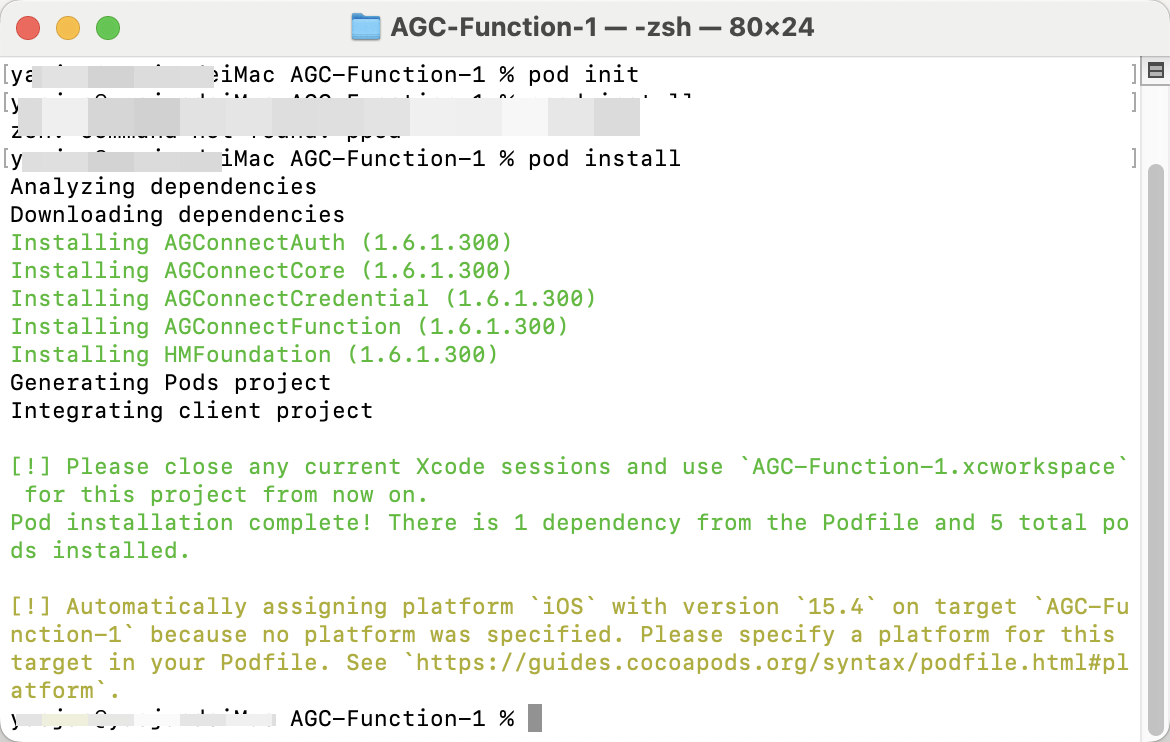
let myHandler = function(event, context, callback, logger)
{
var res = new context.HTTPResponse(context.env, {
"res-type": "context.env",
"faas-content-type": "json",
}, "application/json", "200");
var year;
if (event.body) {
var _body = JSON.parse(event.body);
year = _body.year;
} else {
year = event.year;
}
var body = {
result: ''
};
body.result = animal(year);
res.body = body;
context.callback(res);
function animal(inputYear) {
var resultString;
if (!isNumber(inputYear)) {
resultString = "input is not a number";
} else {
var remainder = inputYear % 12;
switch (remainder) {
case 0:
resultString = "Monkey";
break;
case 1:
resultString = "Chicken";
break;
case 2:
resultString = "Dog";
break;
case 3:
resultString = "Pig";
break;
case 4:
resultString = "Mouse";
break;
case 5:
resultString = "Cow";
break;
case 6:
resultString = "Tiger";
break;
case 7:
resultString = "Rabbit";
case 8:
resultString = "Dragon";
break;
case 9:
resultString = "Snake";
break;
case 10:
resultString = "Horse";
break;
case 11:
resultString = "Sheep";
break;
default:
resultString = "No symbolic Animal";
}
}
return resultString;
}
function isNumber(input) {
if (parseInt(input).toString == "NaN") {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
};
module.exports.myHandler = myHandler;
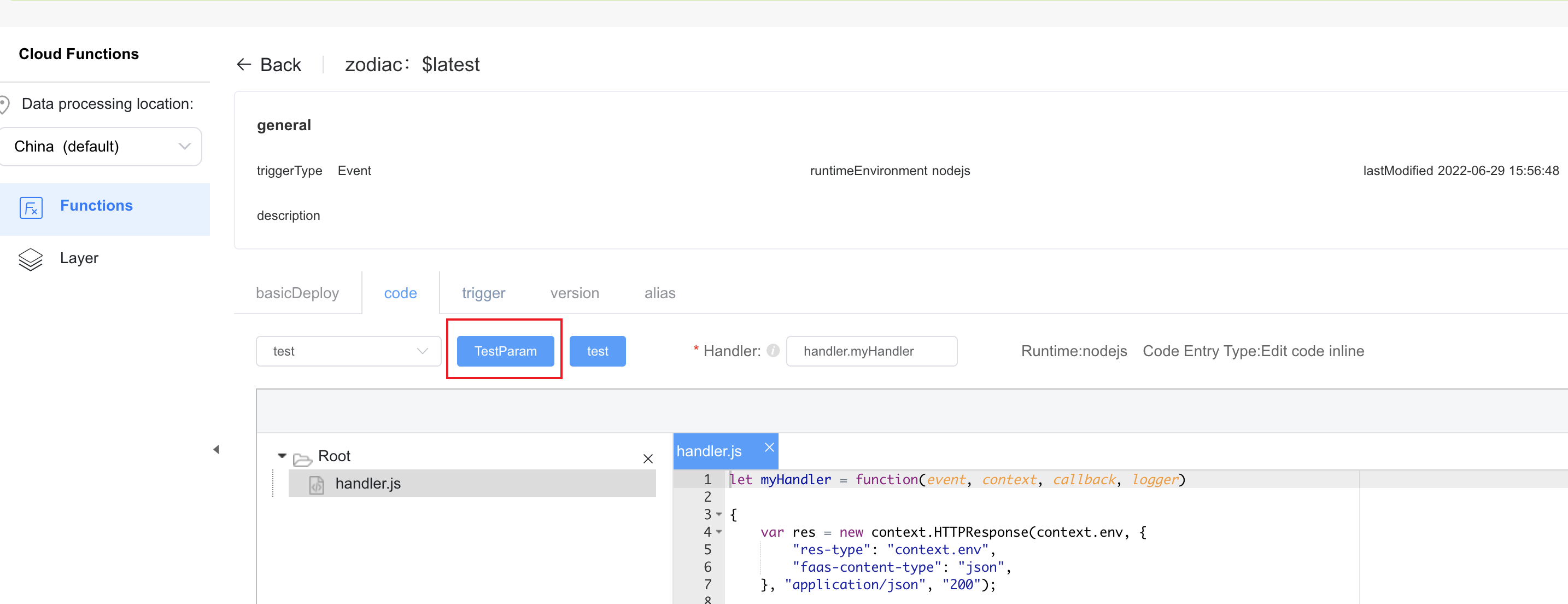
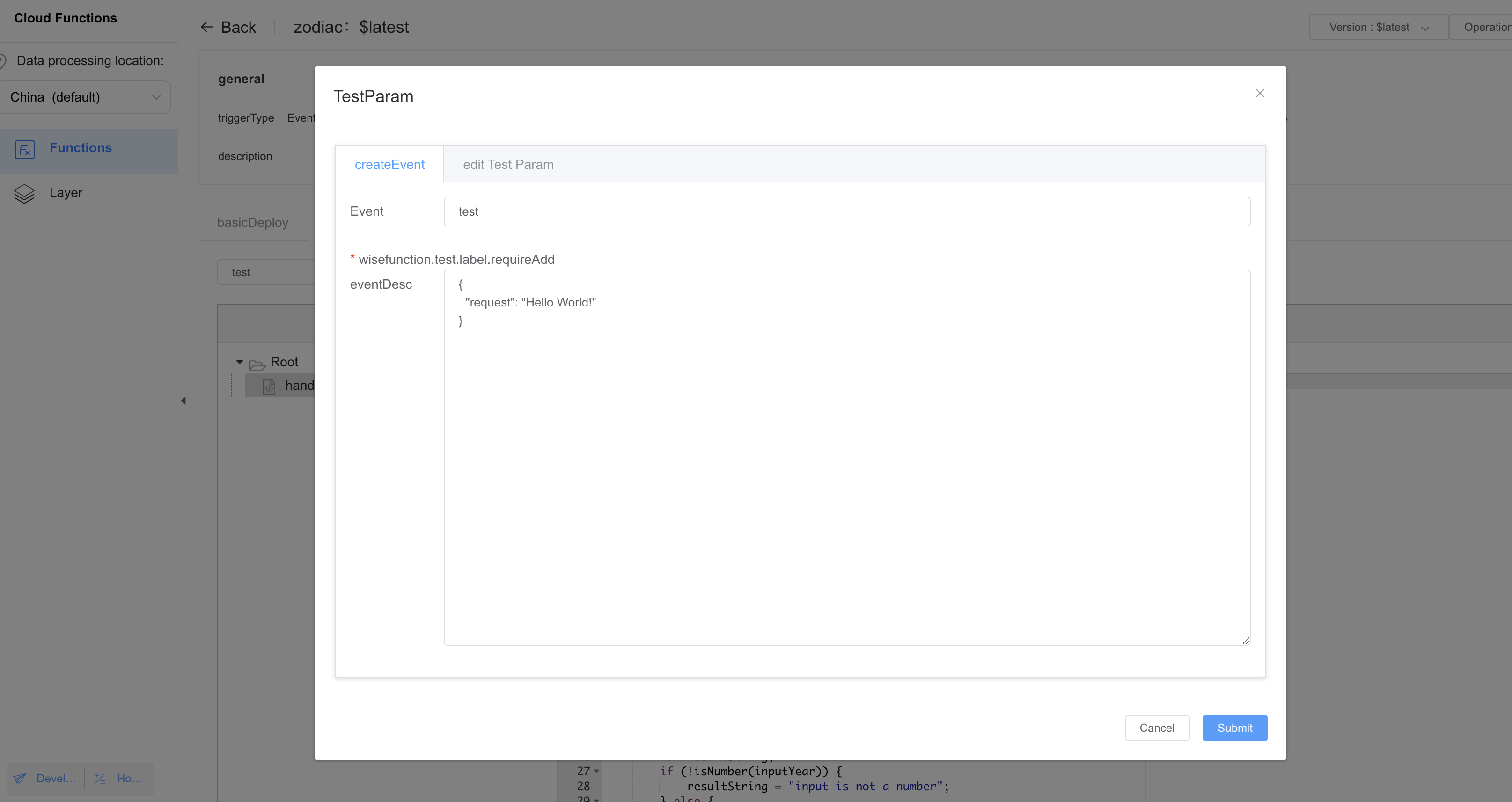
{
"year": 2020
}
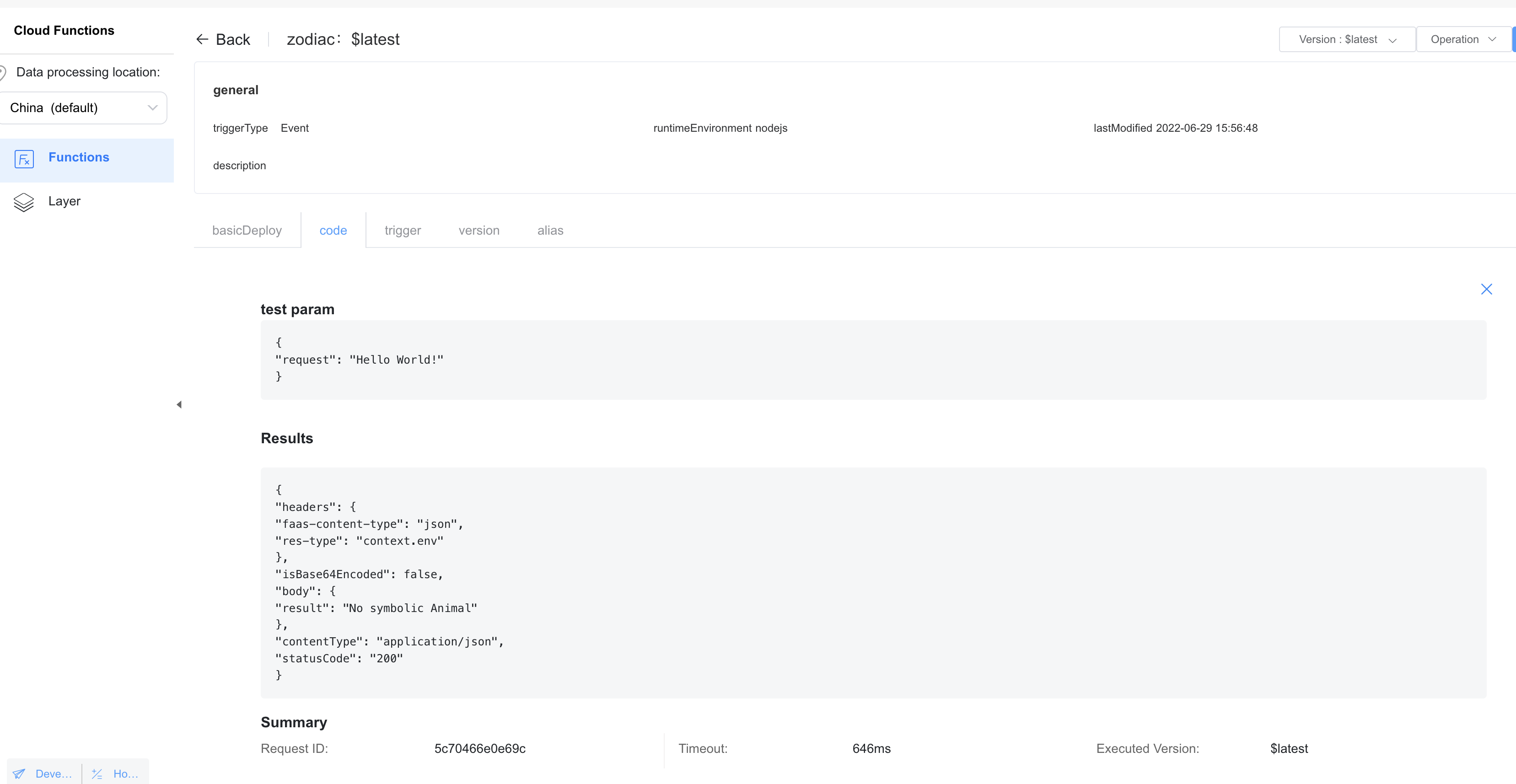
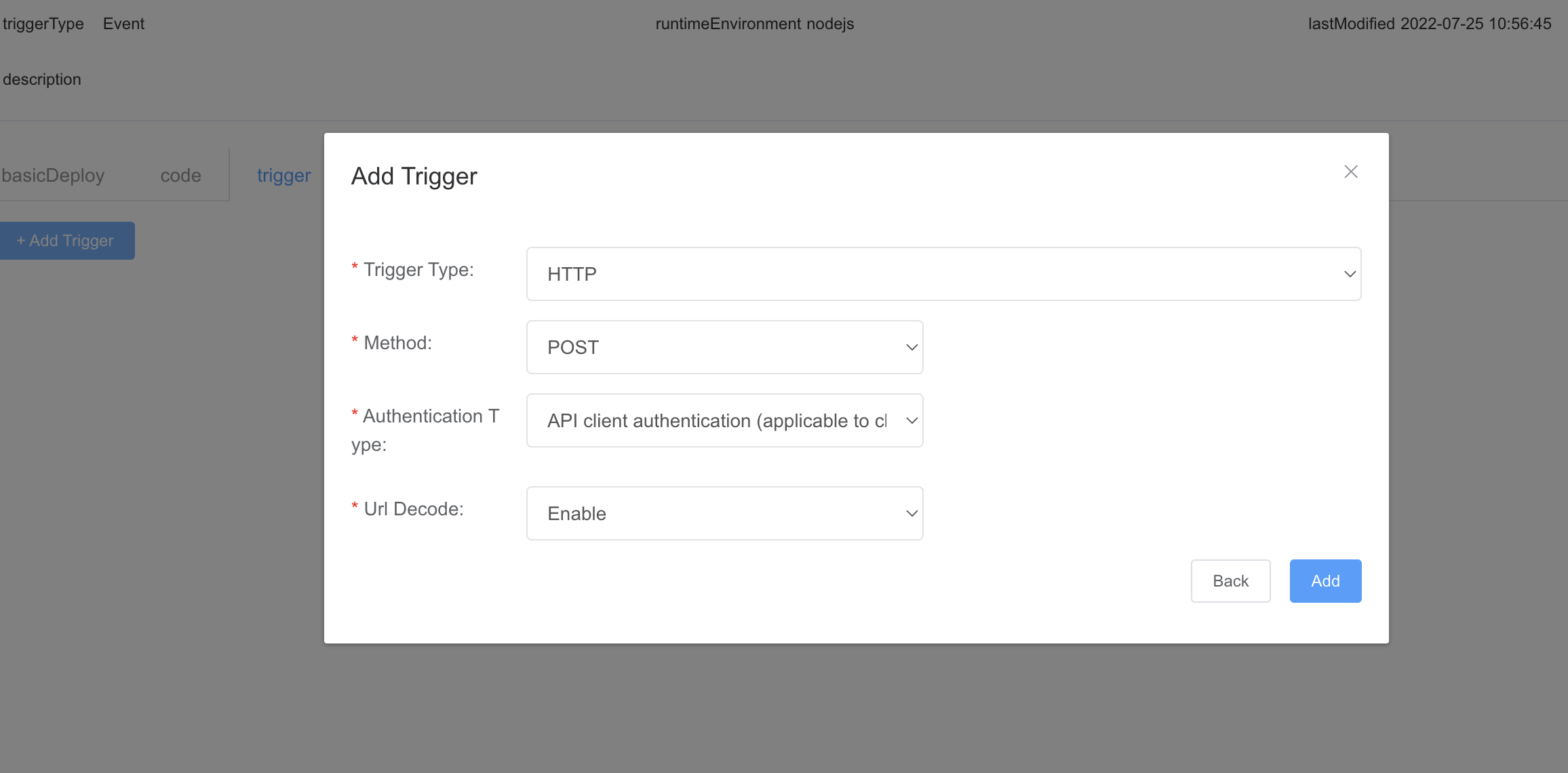
Parameter | Description |
Trigger Type | Set this parameter to HTTP. |
Method | Set this parameter to POST, which is currently the only supported method by HTTP triggers. |
Authentication Type | Authentication type of the HTTP trigger to be added.API client authentication (applicable to clients): gateway authentication on the client, which is applicable only to function calls from the app client.API client authentication (applicable to Server): gateway authentication on the cloud, which is applicable only to function calls from the app server. |
Url Decode | Indicates whether to use the URLDecoder to decode the body of an HTTP-based function trigger request whose contentType is application/x-www-form-urlencoded and forward the decoded result to the function. |
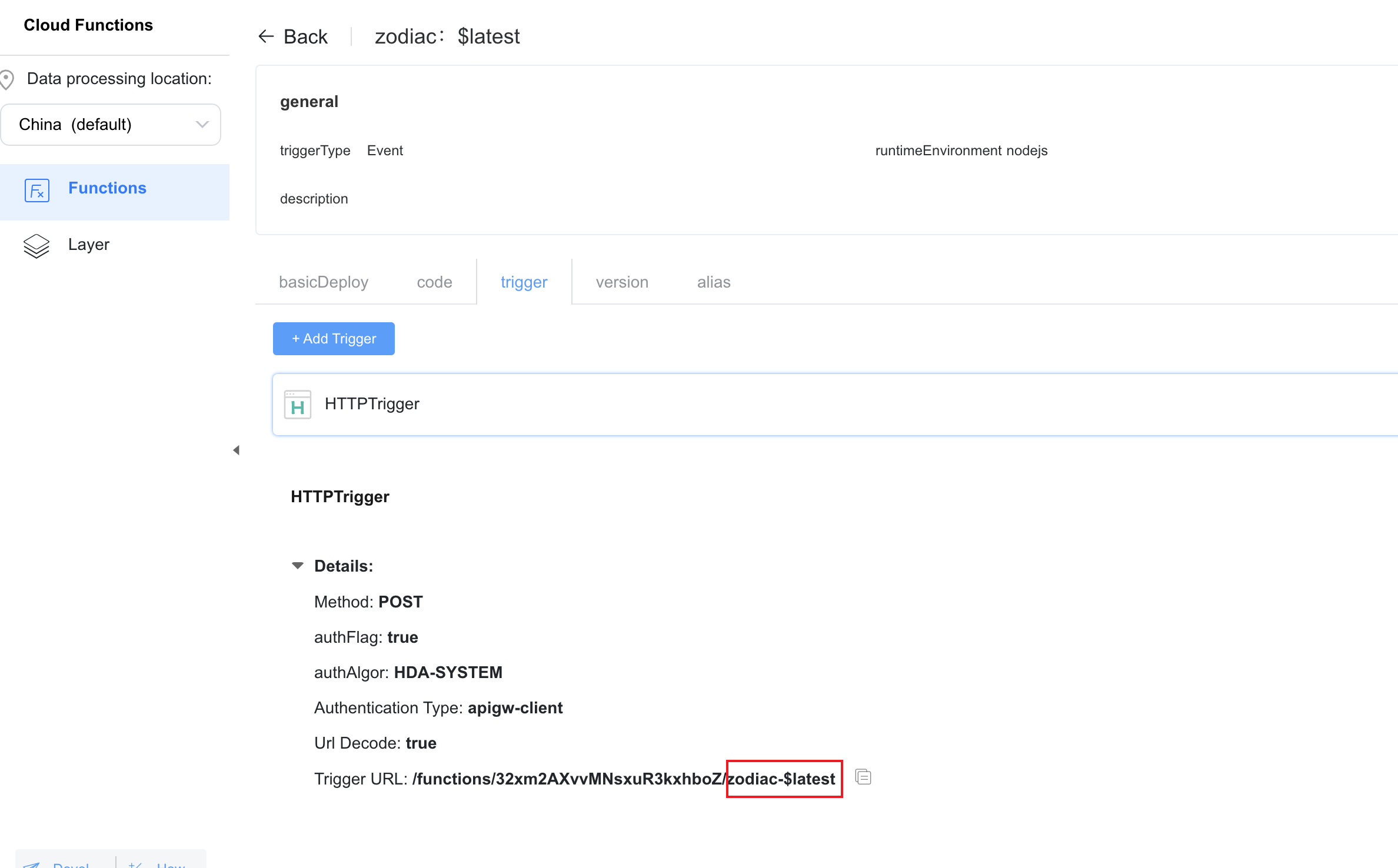
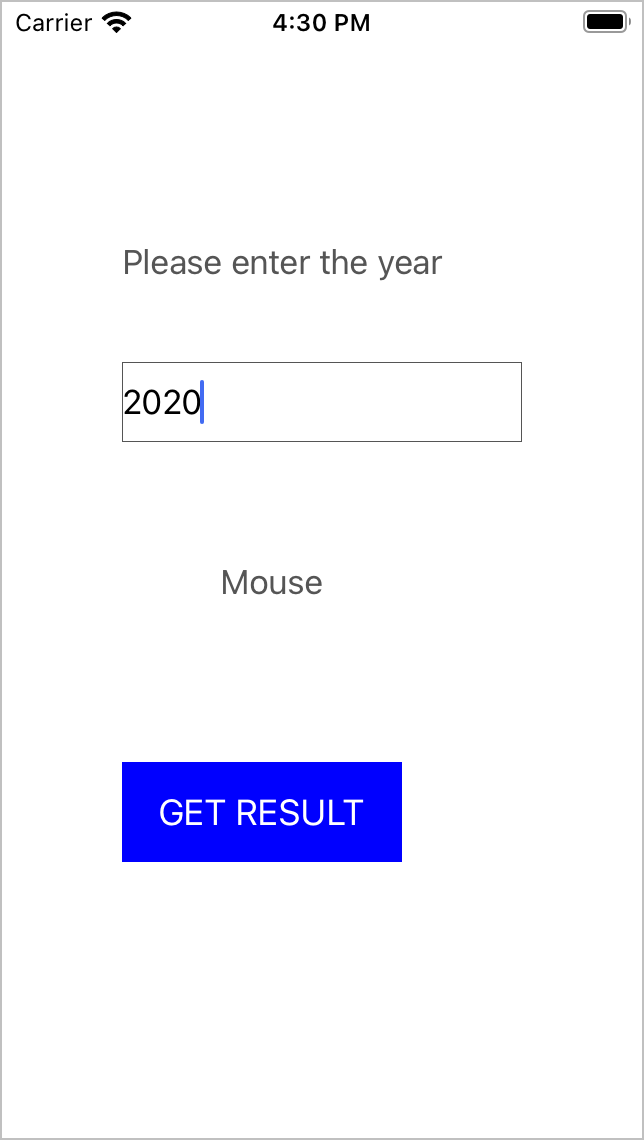
In this codelab, you can create a layout shown in the following figure in your iOS project. On the page, a result returned by a cloud function is displayed after a year is entered.
Sample code:
let yearTextField = UITextField(frame: CGRect(x: 60, y: 180, width: 200, height: 40))
let zodiacLabel = UILabel(frame: CGRect(x: 60, y: 260, width: 150, height: 60))
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let welcomeLabel = UILabel(frame: CGRect(x: 60, y: 100, width: 200, height: 60))
welcomeLabel.textColor = UIColor.darkGray
welcomeLabel.text = "Please enter the year"
self.view.addSubview(welcomeLabel)
yearTextField.layer.borderWidth = 0.5
yearTextField.layer.borderColor = UIColor.darkGray.cgColor
self.view.addSubview(yearTextField)
zodiacLabel.textAlignment = .center
zodiacLabel.textColor = UIColor.darkGray
self.view.addSubview(zodiacLabel)
let functionButton = UIButton(frame: CGRect(x: 60, y: 380, width: 140, height: 50))
functionButton.backgroundColor = UIColor.blue
functionButton.setTitle("GET RESULT", for: .normal)
functionButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(triggerFunction), for: .touchUpInside)
self.view.addSubview(functionButton)
}
import AGConnectCore
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
AGCInstance.startUp()
return true
}
@objc func triggerFunction() {
let num = yearTextField.text ?? ""
let callable = AGCFunction.getInstance().wrap("zodiac-$latest")
callable.call(with: ["year":num]).onSuccess { (result) in
let response = result?.value(with: NSDictionary.self) as! NSDictionary
let zodiac = response["result"] as! String
self.zodiacLabel.text = zodiac
}.onFailure { (error) in
}
}
Well done. You have successfully built your first app that integrates Cloud Functions and learned how to: